- Osteoarthritis is a joint disease causing stiffness, pain, and swelling, affecting older and younger adults.
- The disease develops due to injuries, genetics, obesity, unhealthy lifestyle, and certain medical conditions.
- Young adults who participate in high-impact activities, have genetic predispositions, unhealthy habits, or carry excess weight are at risk.
- Platelet treatment, physiotherapy, weight management, and medications effectively manage osteoarthritis symptoms.
- Early detection and a proactive approach to health can slow disease progression, maintaining joint mobility and function.
Osteoarthritis, a type of joint disease that causes stiffness, pain, and swelling, is typically associated with aging. However, this condition can affect young adults as well. It is a common issue affecting millions worldwide, regardless of age. If you are a young adult experiencing joint problems, it’s essential to understand why you might be developing osteoarthritis. Here’s what you need to know about the disease, why young adults can get it, and ways to deal with and prevent it.
What is Osteoarthritis?
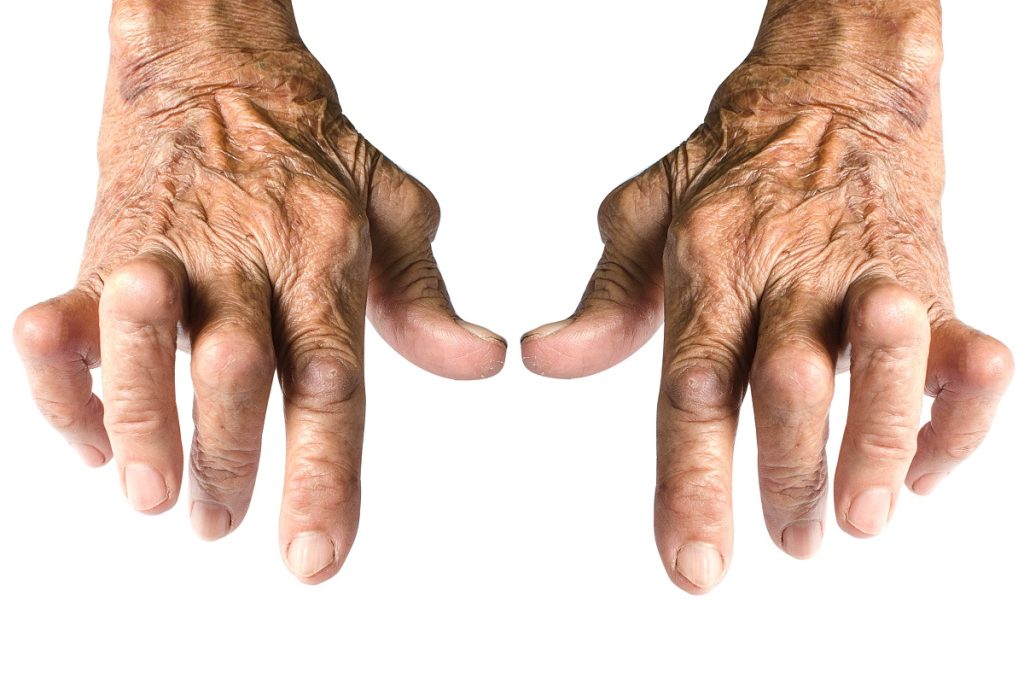
Osteoarthritis is arthritis that affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling. It occurs when the cartilage between bones breaks down, leading to bone-on-bone contact and friction within the joint. This can cause inflammation and damage to surrounding tissues.
The most commonly affected joints in osteoarthritis are the hands, knees, hips, and spine. It is a progressive disease, meaning it worsens over time. While the exact cause of osteoarthritis is unknown, genetics, obesity, joint injuries, and age can increase the risk of developing this condition.
Why Do Young Adults Develop Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is often associated with aging, as the degeneration of cartilage and joints is a natural part of aging. Here are some reasons young adults may develop it:
1. Injury and Overuse
Young adults who engage in sports or workout extensively are at risk of developing osteoarthritis due to overuse and injury. Every person has limits in terms of physical activity, and doing too much can cause damage to joints. Injuries to the cartilage, tendons, and ligaments can speed up the development of osteoarthritis. If you have experienced physical trauma or engage in high-impact activities, taking a break and seeking medical attention when required is essential.
2. Genetics

Genetics can play a significant role in developing osteoarthritis in young adults. If your family has a history of osteoarthritis, you might be more at risk of developing this condition. Genetic factors affect the likelihood of developing the condition and its severity. Research has also shown that specific genetic markers can be linked with the development of osteoarthritis in young adults.
3. Obesity
Being overweight or obese is another common cause of osteoarthritis in young adults. Excess weight puts a lot of pressure on the joints, especially the knees and hips. Studies have shown that obese individuals are more likely to develop OA than non-obese individuals.
4. Unhealthy Lifestyle
Unhealthy habits like smoking and alcohol consumption can increase the likelihood of developing osteoarthritis. Both unhealthy practices can increase inflammation and introduce harmful substances into the body, worsening the condition.
5. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can also cause osteoarthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis, for example, is an autoimmune disorder that can damage your joints and cause osteoarthritis. Other conditions, such as gout and joint hypermobility syndrome, can contribute to the development of osteoarthritis.
Dealing With The Disease
There are various ways young adults can deal with osteoarthritis and improve their quality of life:
Platelet Treatment
Your platelet cells contain growth factors that can help repair damaged tissue. Platelet-rich plasma treatment involves injecting your platelets into the affected area to reduce pain and inflammation, stimulate tissue repair, and slow down the progression of osteoarthritis. It can also improve mobility and joint function.
Physiotherapy

Physiotherapy can help reduce pain, and improve mobility and flexibility in the affected joints. A physiotherapist will work with you to develop an exercise plan that caters to your needs and helps manage pain.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing osteoarthritis symptoms. Excess weight strains the joints, leading to increased pain and inflammation. Losing weight can reduce stress on your joints and improve mobility.
Medications
Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help relieve pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis. Sometimes, your doctor may prescribe stronger painkillers or corticosteroids to manage severe symptoms.
Osteoarthritis, while associated with aging, can also affect young adults due to genetic predisposition and certain medical conditions. It’s crucial to remember that despite its challenges, osteoarthritis is manageable. A combination of treatments can significantly improve quality of life. If you’re a young adult experiencing joint discomfort, seeking medical advice early is vital. Early detection and management can slow down the progression of the disease and help maintain joint mobility and function. Remember, a proactive approach to your health can make a difference.